Air compressors are the workhorses of a construction or industrial project. They are used to operate various pneumatic tools and equipment, such as jackhammers, concrete breakers, and nail guns, as well as inflate tires of forklifts, loaders, and other equipment.
Depending on the size of the air compressor, it can power anything from a handheld spray paint gun to a rock drill used to make blast holes in mining sites.
Reliable, versatile and safe, air compressors are also convenient and cost-effective—instead of having multiple power sources for several tools, a single air compressor can power a single tool as needed. Additionally, air compressors are often quieter, and because they have fewer parts than some other kinds of power sources, they are easier to maintain and less likely to break down.
If you’re considering getting an air compressor for your project, you likely have many questions, such as:
- How does an air compressor work?
- What are the types of air compressors available?
- What are the applications of an air compressor on a construction site?
Below, we go into the basics of air compressor mechanics, answer these questions and more.
How Do Air Compressors Work? Basic Principles
There are two main categories of air compressors: positive displacement and dynamic. This article primarily focuses on positive displacement air compressors as they are the most commonly used in commercial and industrial settings.
Although positive displacement air compressors come in various shapes and sizes, they all work on the same fundamental principle of taking in air from the surroundings, compressing it, and releasing it at a higher pressure.
Atmospheric air contains a certain amount of energy, and when an air compressor compresses it, this energy becomes concentrated into a smaller volume. This process increases the pressure of the air, allowing it to be used in a wide range of applications.
The Key Components of an Air Compressor
- Intake Valve: This is the initial point where air enters the system.
- Compressor or Pump: This component consists of either a piston or a rotating mechanism, which compresses the air.
- Air Receiver or Tank: The compressed air is stored in a tank, allowing the compressor to stop running once it is full.
- Discharge Valve: This releases the compressed air as required, depending on the attached tool or equipment.
- Pressure Controls: Air compressor pressure controls, such as pressure switches and relief valves, ensure the compressor operates within safe limits. The pressure switch automatically turns off the compressor pump when the tank reaches its maximum pressure, while the pressure relief valve releases excess pressure to prevent damage to the system.
- Regulator: This reduces the air from the tank to a lower, controlled pressure suitable for your tool or application.
Apart from the parts mentioned above, an air compressor typically also has a control system. It allows users to optimize the performance of an air pressure compressor and monitor or maintain desired pressure levels within the tank and output system. Additionally, it tracks parameters like oil levels, air quality and temperature, as well as shuts down the compressor in case of problems.
The Compression Cycle
The air compressor’s compression cycle can be summarized into the following steps:
- Air Intake: As the compressor begins its cycle, the intake valve opens, allowing air to be drawn into the compression chamber.
- Compression: The compressor mechanism activates, causing the air to be compressed. During this step, the air pressure increases and energy is stored within it.
- Storage: Once the air reaches the desired pressure level, it is sent to the storage tank, where it is held for future use.
- Pressure Switch Cut-in: When the pressure reaches the preset cut-in point of the pressure switch, it sends a signal to the compressor motor, causing it to turn off. This keeps the pressure inside the tank from exceeding the maximum level.
- Release: When you need to use the compressed air, the discharge valve opens, and the air is released from the tank to the tool or equipment.
- Regulator Steady State: The regulator continuously reduces the pressure from the air in the tank to the lower pressure required for your tool or application.
- Pressure Switch Cut-out: When it reaches the preset cut-out point of the pressure switch, the pressure switch sends a signal to the compressor motor to turn on again.
Types of Air Compressors
Positive displacement air compressors work by mechanically reducing air volume to increase pressure. As the volume of air decreases, the pressure increases proportionally. This type of compressor is ideal for applications that require continuous airflow at stable pressures. They are commonly used in construction projects due to their efficiency and ability to handle various demands.
The following is a brief overview of two of the most commonly used positive displacement air compressors.
Reciprocating Air Compressors
Reciprocating air compressors, also known as piston compressors, are among the most commonly used types of positive displacement air compressors in the construction industry.
These compressors operate on the principle of a reciprocating motion, utilizing a piston within a cylinder. As the piston moves downward, air is drawn into the cylinder. When the piston moves upward, the air is compressed and then discharged.
Pros of Reciprocating Air Compressors
- Suitable for Small to Medium-sized Applications: Reciprocating air compressors work best in powering smaller pneumatic tools and equipment used in construction, such as nail guns, sanders, impact wrenches, tire inflators and paint sprayers.
- Lower Initial Cost: The purchase price of a reciprocating air compressor is typically much lower than a rotary screw compressor of similar output.
- Suitable for Intermittent Use: The straightforward design of a reciprocating air compressor is well-suited for stop-and-start operations.
- Can Generate High Pressures: Depending on the model and specifications, a reciprocating compressor can achieve very high pressures of up to 300+ psi. This makes it suitable for operating more energy-intensive pneumatic tools like sandblasters and jackhammers.
Cons of Reciprocating Air Compressors
- Requires Regular Maintenance: Compared to rotary screw compressors, air compressors may need more frequent maintenance. If you purchase one, you can expect it to require frequent oil changes, filter replacements, and piston/valve checks.
- Can Be Noisy: Due to its reciprocating motion, this type of compressor tends to produce a lot of noise and vibration. Users may require hearing protection.
- Limited Ability to Scale Up for Larger Applications: While there are bigger, heavier-duty reciprocating compressors, they are limited in their overall output and efficiency. This makes them less suitable for large-scale construction and industrial applications compared to rotary screw compressors.
Rotary Screw Air Compressors
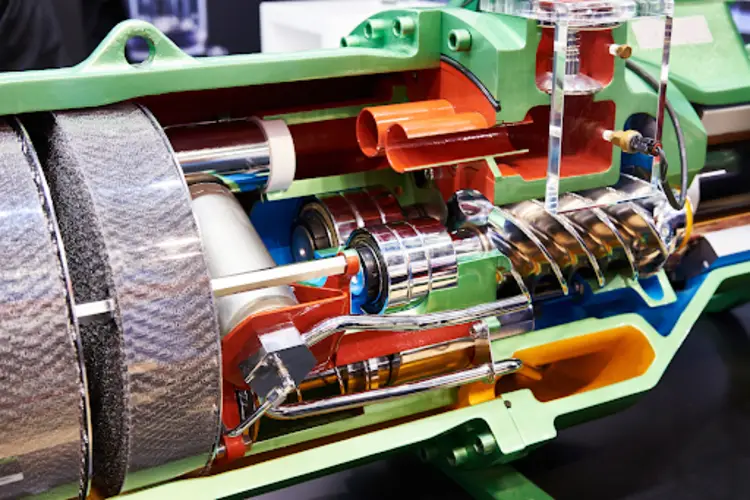
Rotary screw air compressors are another common type of positive displacement compressor employed in the construction industry. They consist of two parallel rotors (screws) enclosed within a casing. The rotors rotate in opposite directions, trapping and compressing the air between them. This type of compressor delivers a continuous flow of compressed air at a constant pressure, making them ideal for applications that require continuous operation.
Pros of Rotary Screw Air Compressors
- Suitable for Continuous and Heavy-duty Operations: Rotary screw compressors offer reliable performance and can handle sustained high-pressure demands.
- Quieter operation: Compared to reciprocating compressors, rotary screw compressors generate less vibration and noise.
- Energy Efficient in Certain Applications: Rotary screw compressors can be more efficient than reciprocating compressors at higher loads and if operated continuously.
- Generally Require Less Maintenance: Rotary screw compressors have fewer parts that are prone to wear and tear than reciprocating compressors. However, it’s essential to remember that they still need upkeep, such as regular oil changes and filter replacements, to keep them working at top performance.
Cons of Rotary Screw Air Compressors
- Higher Initial Cost Compared to Reciprocating Compressors: The upfront cost of a rotary screw compressor is typically higher than its reciprocating counterpart. Be sure to compare models and types if this is a primary concern.
- Can Be Less Energy Efficient in Intermittent Applications: At low or intermittent loads, rotary screw compressors may be less energy-efficient than reciprocating compressors, as they have a more complex design and higher energy consumption at idle conditions.
Reciprocating and rotary screw air compressors both have their advantages and disadvantages.
The choice between these two popular positive displacement compressors depends on your construction project’s specific needs and budget. Additionally, it’s essential to factor in noise levels, energy efficiency, and pressure capabilities when making your decision.
Applications in Construction
Air compressors can significantly increase efficiency and productivity in construction applications. Compressors eliminate the need for manual labor in certain tasks, reducing the time required to complete projects and increasing the overall effectiveness of construction teams.
Also, air compressors are versatile tools that can be used in numerous applications, making them a wise investment for cost-conscious construction firms.
- Air compressors make it possible to utilize air-powered or pneumatic tools such as air hammers, nail guns, sanders and drills.
Air-powered or pneumatic tools can generate much more power than mains-powered or electric tools, making them ideal for tackling jobs like breaking concrete and grinding metal. Using pneumatic tools helps construction crews complete tasks faster, boosting their efficiency and productivity.
Additionally, pneumatic tools are safe and straightforward to operate. Since they rarely malfunction, they help minimize downtime. Using these air compressor-powered tools results in increased efficiency, reduced fatigue, and improved accuracy.
- Air compressors are also indispensable for tasks like material handling and transport. In construction projects, materials like sand, cement, and gravel must be transported from one location to another. Using air compressors to power conveyance systems makes the handling processes more efficient, saving both time and effort.
- Air compressors can be used to clear out water lines and fill air tanks on site.
Safety Considerations When Using Air Compressors
As mentioned, air compressors are safe to use. However, they can pose serious safety dangers to operators and those around them if they’re not used correctly. Below are some critical safety measures that should be taken when operating air compressors to ensure safe and efficient usage.
Use the Right Tool for the Job
Using the correct tool minimizes misuse and the risk of injury. Before using an air compressor to power a tool or for an application, it’s best first to consider:
- The required airflow in cubic feet per minute (CFM) for your specific task
- The maximum pressure in pounds per square inch (PSI) that the compressor can handle
- The pressure, measured in PSI, needed for the tool
Generally, the pressure and airflow your compressor produces must align with the pressure required by the tool. Mismatching can result in damage to the tool, wasted energy and safety hazards.
Inspect Tools for Wear and Tear
This is crucial for preventative maintenance and avoiding accidents.
Avoid Makeshift Connections
Improper connections can create safety hazards due to leaks and pressure issues.
Wear Protective Gear
Make sure to don sufficient protective gear when using an air compressor or air compressor-powered tool. This includes safety goggles, hearing protection, gloves and appropriate clothing.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
Before you operate an air compressor, first read the manual that comes with it. Doing so helps ensure that you understand how to operate the compressor safely.
The Advantages of Renting an Air Compressor
Choosing between renting and purchasing an air compressor can be difficult, and which is the right option for you depends on factors such as how frequently you plan on using an air compressor and your budget.
To help you make an informed decision, the following are some reasons why renting an air compressor might be a better choice.
Lower Upfront Costs
Purchasing an air compressor can be a significant investment, especially for smaller businesses and occasional users. Renting an air compressor allows you to avoid the upfront costs associated with buying.
Flexible Rental Options
Renting air compressors allows you to choose the right machine for your needs and budget. At National Dispatching, we offer a wide range of options, allowing you to select the best air compressor for your project without worrying about breaking the bank.
No Depreciation Costs
Owning an air compressor means eventually dealing with depreciation costs. You can avoid this issue by renting an air compressor, as the air compressor rental company handles equipment depreciation.
Minimal Maintenance Responsibility
One of the key benefits of renting an air compressor is that you don’t have to worry about maintenance. Rental companies are responsible for ensuring their equipment is in excellent condition, meaning you’ll receive a well-maintained air compressor every time you rent.
No Long-term Storage Requirements
You won’t have to worry about where to put your air compressor when you’re not using it. When you rent an air compressor, you return it to the rental company once your project is complete. This reduces storage space requirements and associated costs.
Immediate Replacement When Needed
If an air compressor malfunctions during your rental period, you won’t have to waste time looking around for someone to repair it before you can get back to work. The rental company will usually replace the faulty equipment promptly. This reduces downtime and ensures your project remains on schedule.
Trust National Dispatching for Quality Air Compressor Rentals
When it comes to air compressor rentals, National Dispatching has you covered. We understand that every project has unique needs, and our top-of-the-line equipment is designed to meet them.
We offer a variety of well-maintained air compressors, pneumatic tools and other essential construction equipment for rent at competitive rates and flexible terms. To rent, simply add your chosen equipment or tools to your cart and follow the checkout instructions.
If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to reach out to us. Our knowledgeable staff is happy to assist you.

